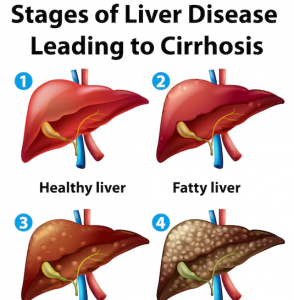
- Medical Treatment and Monitoring: Consult a hepatologist or gastroenterologist for appropriate medical management. Treatment may include medications to manage symptoms, address underlying causes, and prevent complications.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sodium intake to manage fluid retention and swelling.
- Abstinence from Alcohol: If alcohol is a contributing factor to liver damage, complete abstinence is essential to prevent further deterioration.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Obesity can worsen liver cirrhosis.
- Monitoring and Support: Regular monitoring of liver function and compliance with medical advice are crucial. Support groups or counseling may also help manage the emotional aspects of living with cirrhosis.
It’s important to emphasize that alternative therapies like sattu and gomutra have not been proven effective for treating liver cirrhosis and should not replace evidence-based medical care. Always consult qualified healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment.
